画像 endocrine and exocrine glands examples 675330-Endocrine and exocrine gland examples
The adrenal gland, which secretes the hormone adenaline from the adrenal medulla into the blood, is an example of an endocrine organ Exocrine glands secrete their products, such as enzymes, into ducts which lead to the target tissues The salivary gland secretes saliva in the collecting duct that leads to the mouthFollow us at https//plusgooglecom/tutorvista/Check us out at http//wwwtutorvistacom/content/biology/biologyiv/chemicalcoordinationanimals/endocrin1 bloodwater concentration detected by hypothalamus receptors 2 ADH is released by hypothalamus 3 kidneys will reabsorb water to concentrate urine thyroid gland only one function = endocrine brain monitors BMR and controls by releasing TRH from hypothalamus = negative feedback loop
Exocrine Vs Endocrine Glands Definition 8 Differences Examples
Endocrine and exocrine gland examples
Endocrine and exocrine gland examples- Adrenal glands, thyroid glands, parathyroid glands are examples of endocrine glands Examples falling under exocrine glands include salivary glands, mammary glands and lacrimal glands The pancreas is the largest endocrine gland found in the body In reality, it is both an endocrine as well as an exocrine glandExamples of exocrine glands




Class 10 Control And Coordination Short Answers Freeguru Helpline
The substances secreted by the glands are often chemical messengers with effect at a distance, for example hormones , but they can also exert an action or an effect directly in the medium in which they are secreted, which gives rise to, in addition to endocrine glands and exocrine, to different types of communication or effect, such as the autocrine effect or the paracrine effectExocrine Glands and Endocrine Glands •Exocrine Glands –Exocrine glands have ducts that carry a secretion to a body surface or an organ cavity –Exocrine glands produce extracellular effects –Example sweat glands release sweat onto the skin •Endocrine Glands –Endocrine glands doName two examples of each exocrine and endocrine glands An exocrine gland is a gland that secretes its products into ducts that lead to the target tissue Examples of exocrine glands are sweat, salivary, sebaceous, mucous gland An endocrine gland is a gland which secretes its products directly into the blood stream
Additionally, the term "gland" does not necessarily mean that the organ is part of the endocrine system For example, sweat glands, salivary glands, glands in mucus membranes, and mammary glands are called exocrine glands, because they secrete substances other than hormones and because they secrete the substances into ducts, not directly into the bloodstream Throughout the embryo development, endocrine glands lack ducts and remain as blocks of tissue So, it secrets chemical substances directly to the blood stream, while exocrine gland secrets its product into a duct However, some glands may have both endocrine and exocrine activities such as the pancreas (Taylor et al, 1998) Exocrine glands are cellular substructures, organs, in a body that provide a system to secrete substances out and external to the body They are distinct from the other type of gland, endocrine, in that exocrine gland secretions end up external to the body, while endocrine secretions go into the bloodstream/internal
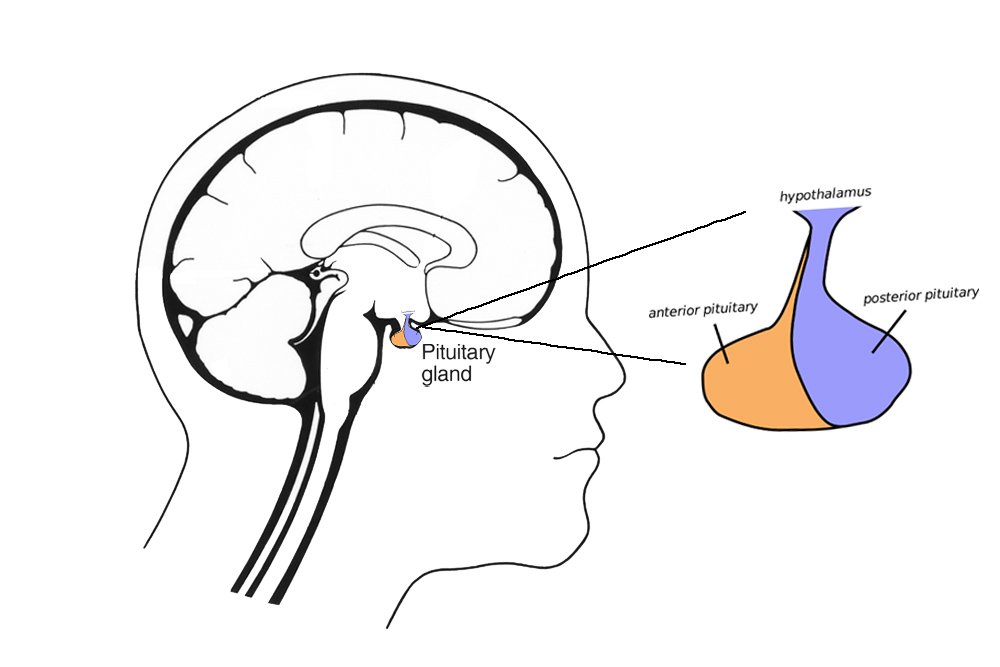
Pituitary Gland It is often considered the most important part of the endocrine system because it produces hormones that control many functions of other endocrine glands When the pituitary gland does not produce one or more of its hormones or not enough of them, it is called hypopituitarism Some exocrine glands are Sweat glands, salivary glands, mucous membranes, mammary glands, sebaceous, and tear glands Substances produced by the exocrine glands travel through ducts and are deposited on epithelial surfaces The endocrine glands are released into the blood and thus reach the cells and organs that require themWhats an exocrine gland gland containg ducts that carry products straight to target cells on the epithelial layers of internal or external body surfaces examples of endocrine




Differences Between Endocrine Glands And Exocrine Glands



Distinguish Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Studyrankersonline
An endocrine gland secretes its products, for example hormones, directly into the blood An example of an endocrine gland is the adrenal gland which secretes adenaline made in the adrenal medulla directly into the blood An exocrine gland secretes its products for example enzymes, into ducts that lead to the target tissueExocrine Gland Endocrine Gland;They're exocrine glands as a result of they secrete merchandise—bile and pancreatic juice—into the gastrointestinal tract by a collection of ducts, and endocrine as a result of they secrete different substances instantly into the bloodstream




Exocrine And Endocrine Glands



Exocrine Glands
Examples of Endocrine and Exocrine Glands By glands It is understood as an organized and hyperspecialized set of cells whose function in the body is the secretion of certain chemical substances such as hormones, lipids or mucus For instance pituitary, thyroid, sweat glands According to the way they have to lead these secreted substancesThere are two different types of glands endocrine and exocrine Endocrine ductless and go directly into the bloodstream Exocrine go through a duct and release secretions through tissues Examples include the sweat glands and the salivary glandsExocrine glands An exocrine gland, unlike an endocrine gland, is a gland that secretes substances (electrolytes, proteins or enzymes) straight to a target site via ducts or tube Some examples include Salivary glands;




Endocrine Gland Definition Development And Classification




The Importance Of Exocrine And Endocrine Glands In Human Body Ppt
Name two examples of each exocrine and endocrine glands An exocrine gland is a gland that secretes its products into ducts that lead to the target tissue Examples of exocrine glands are sweat, salivary, sebaceous, mucous gland An endocrine gland is a gland which secretes its products directly into the blood stream A gland is a functional unit of cells that works together to create and release a product into a duct or directly to the bloodstream Two principal types of glands exist exocrine and endocrine The key difference between the two types is that, whereas exocrine glands secrete substances into a ductal system to an epithelial surface, endocrine glands secreteFunctioning as an exocrine gland, the pancreas excretes enzymes to break do View the full answer Transcribed image text Question 62 3 pts Why is the pancreas both an exocrine and an endocrine gland?



7 Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands With Examples Viva Differences



Endocrine Vs Exocrine Gland Defintion Functions And Differences
Difference # Exocrine Gland 1 Exocrine gland are the duct glands They are attached with a specific duct 2 The secretory products are enzymes, mucous and other substance 3 The Secretions are released to the outer surface of the body or to some internal organ through a Enzymes are biological catalysts, which accelerate chemical reactions The thyroid gland, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands are the examples of endocrine glands The gastric glands, salivary glands, and sweat glands are examples of exocrine glands However, some glands such are liver and pancreas may serve as both endocrine and exocrine glandsThere are two types of gland Endocrine glands are ductless glands and release the substances that they make (hormones) directly into the bloodstream These glands form part of the endocrine system and information on them is included in this website There is another type of gland called an exocrine gland (eg sweat glands, lymph nodes)



The Endocrine System



The Endocrine System
The liver and pancreas are each exocrine and endocrine glands;1 The exocrine gland sends their secretions through ducts directly to target organs of the body 1 Endocrine glands are the ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones directly into the blood 2 Ex Salivary gland, pancreas, etc 2 ExThyroid, pituitary glandetc 1 Ducts Endocrine glands do not utilize ducts or tubes to release their secretions, while exocrine glands require some ducts for transportation of their secretions For this reason the exocrine glans are classified into two types according to the duct types Simple exocrine gland This has only one single duct or unbranched simple ducts for



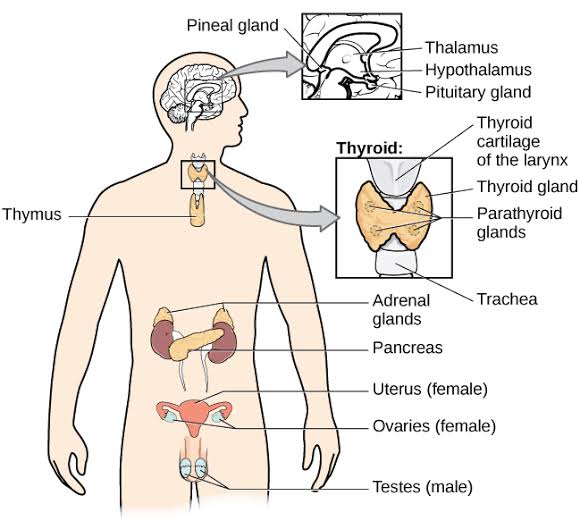
Glands And Hormones In Human Body




Lesson Explainer Action Of Hormones Nagwa
Endocrine and Exocrine Glands 21 By gland It i undertood a an organized and hyperpecialized et of cell whoe function in the body i the ecretion of certain chemical ubtance uch a hormone, lipid or mucuAccording to the way they have t Content Examples of endocrine cells; Exocrine glands are classified as merocrine, apocrine and holocrine, depending on their mode of secretion All these are able to discharge their products via duct system All enzyme secreting glands of GI tract or pancreatic acini are merocrine type No part of secretory cell is lost during secretion which takes place by exocytosis Mammary glands, which secrete milk, are Some glands are both exocrine and endocrine in nature The pancreas is a classic example of such a gland The pancreas releases important hormones (insulin and glucagon) to the blood stream to



1




Differences Between Exocrine And Endocrine Glands Online Science Notes
1 Discrete Endocrine Glands They include the pituitary gland (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal and pineal glands 2 Endocrine component of glands with both an Endocrine and an Exocrine Function They include theExocrine Glands Exocrine glands have ducts and they secrete onto a surface examples of exocrine glands are sebaceous and sweat glands (in the skin), salivary glands (oral), Brunner's glands So, we have covered their basic structure and function in tissue types, and we have looked at several examples of exocrine glands in other topicsUse examples of the secretory products to explain



Difference Between Exocrine Glands And Endocrine Glands Diferr




Introduction To Endocrine System Basic Definition Examples Diagrams
Exocrine glands (not part of the endocrine system) secrete products that are passed outside the body Sweat glands, salivary glands, and digestive glands are examples of exocrine glands The roles of hormones in selecting target cells and delivering the hormonal message An exocrine gland is a gland that secretes its products into ducts that lead to the target tissue Examples of exocrine glands are sweat, salivary, sebaceous, mucous gland Examples of endocrine glands are pituitary gland, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, adrenal glandsAn exocrine gland is a gland that secretes its products into ducts that lead to the target tissue Examples of exocrine glands are sweat, salivary, sebaceous, mucous gland An endocrine gland is a gland which secretes its products directly into the blood stream Examples of endocrine glands are pituitary gland, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland




Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Brainly In
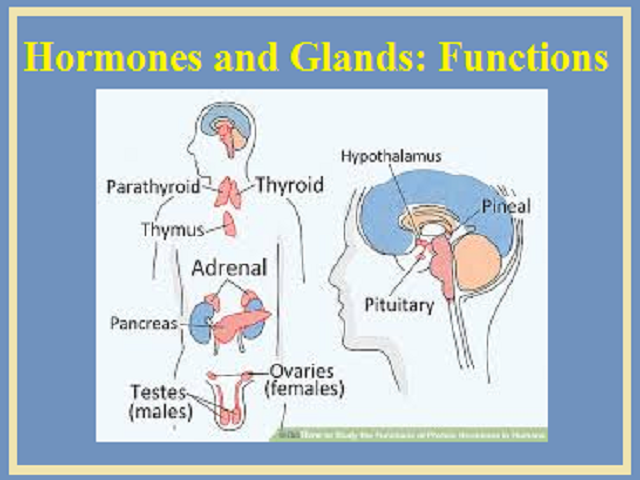



Glands And Hormones In Human Body
The human body has many glands which produce many secretions, such as sweat, saliva, oil and hormones Anatomically, these glands are broadly classified into two types based on the presence or absence of ducts Endocrine glands are the glands that secrete hormones without ducts, while exocrine glands secrete hormones through ducts The exocrine glands have the rapid effect as compared to the endocrine glands The exocrine glands have shorter duration effect than the endocrine glands Salivary, sweat, and digestive are some examples of exocrine glands, whereas pineal gland, pituitary gland, and parathyroid gland are the some of the examples of endocrine glands Examples of exocrine glands are sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, bileproducing glands, prostate, sebaceous, and mucous glandsThese glands can be further classified based on the structure, the method of secretion and the product secreted



Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Definition Types Features Functions
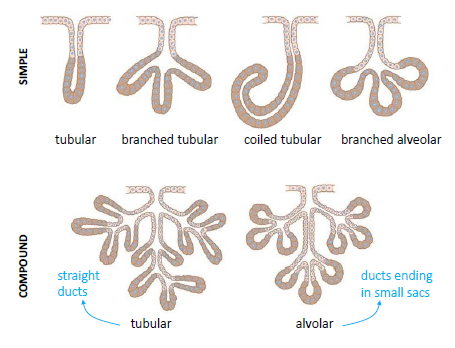



How Are Exocrine Glands Classified Socratic
Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstreamThe pancreas The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ Why are exocrine glands not part of the endocrine system?
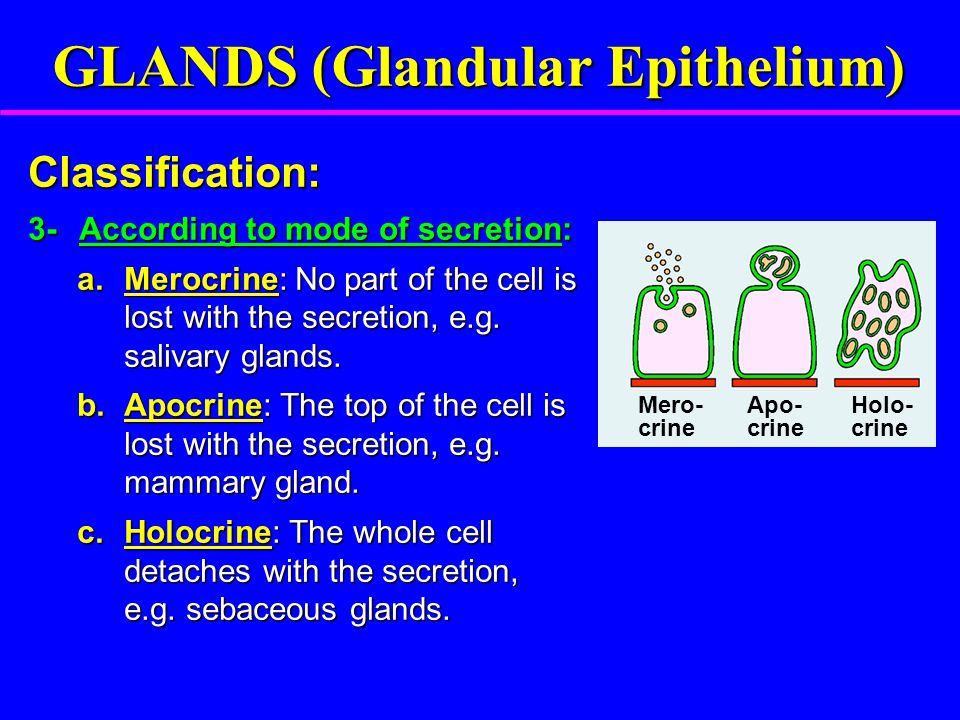



How Do Apocrine Exocrine Merocrine And Holocrine Glands Differ Socratic
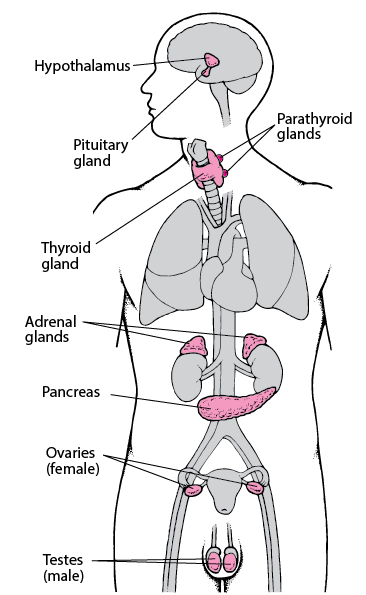



Endocrine Glands Hormonal And Metabolic Disorders Merck Manuals Consumer Version
What is an example of the exocrine glands oil glands, sweat glands, pancreas Endocrine Glands Secrete hormones and are powerful chemical messengers No ductwork and the substances are just dumped outside of the gland and eventually travel into the bloodstream What is an example of the endocrine glands Pituitary gland, thyroid gland What are four examples of exocrine glands?




The Endocrine System Hormones Medical Terminology For Cancer



अन त एव ब ह यय स त र व ग र थ Endocrine And Exocrine Gland In Hindi Part 21 Youtube




Exocrine Vs Endocrine Glands Definition 8 Differences Examples
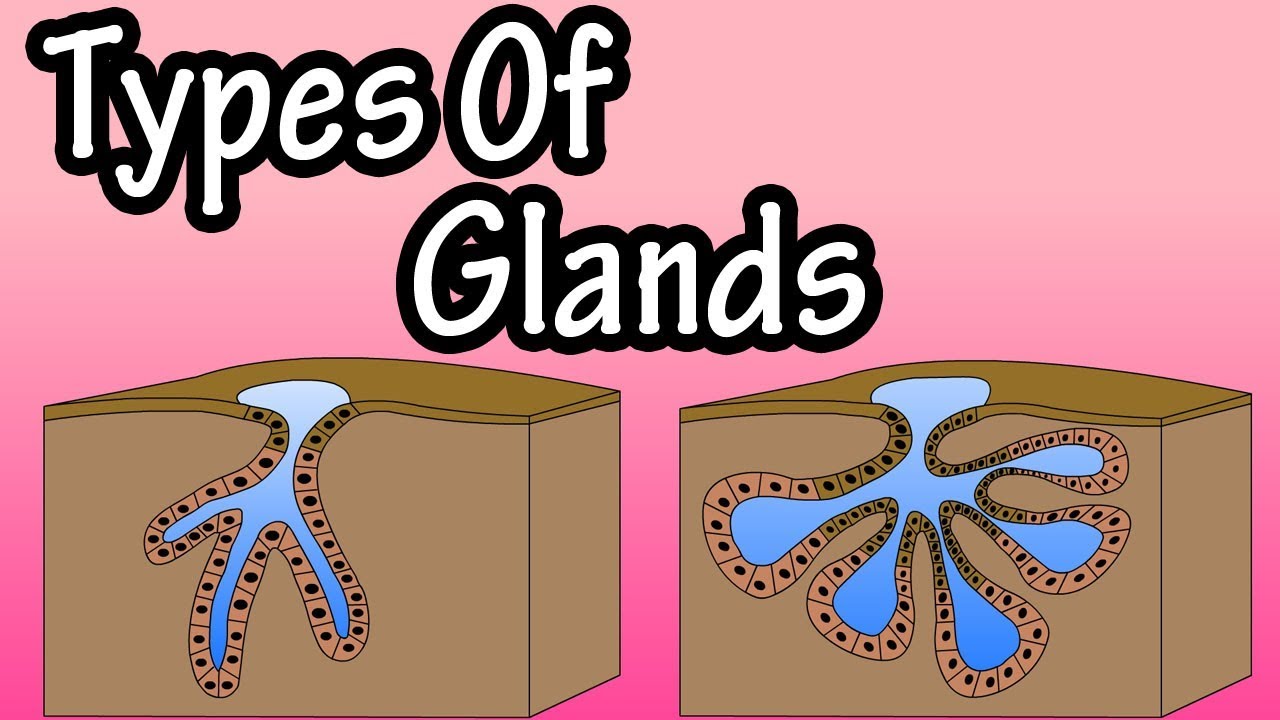



Glands What Are Glands Types Of Glands Merocrine Glands Apocrine Glands Holocrine Glands Youtube




An Overview Of The Endocrine System Anatomy And Physiology Ii
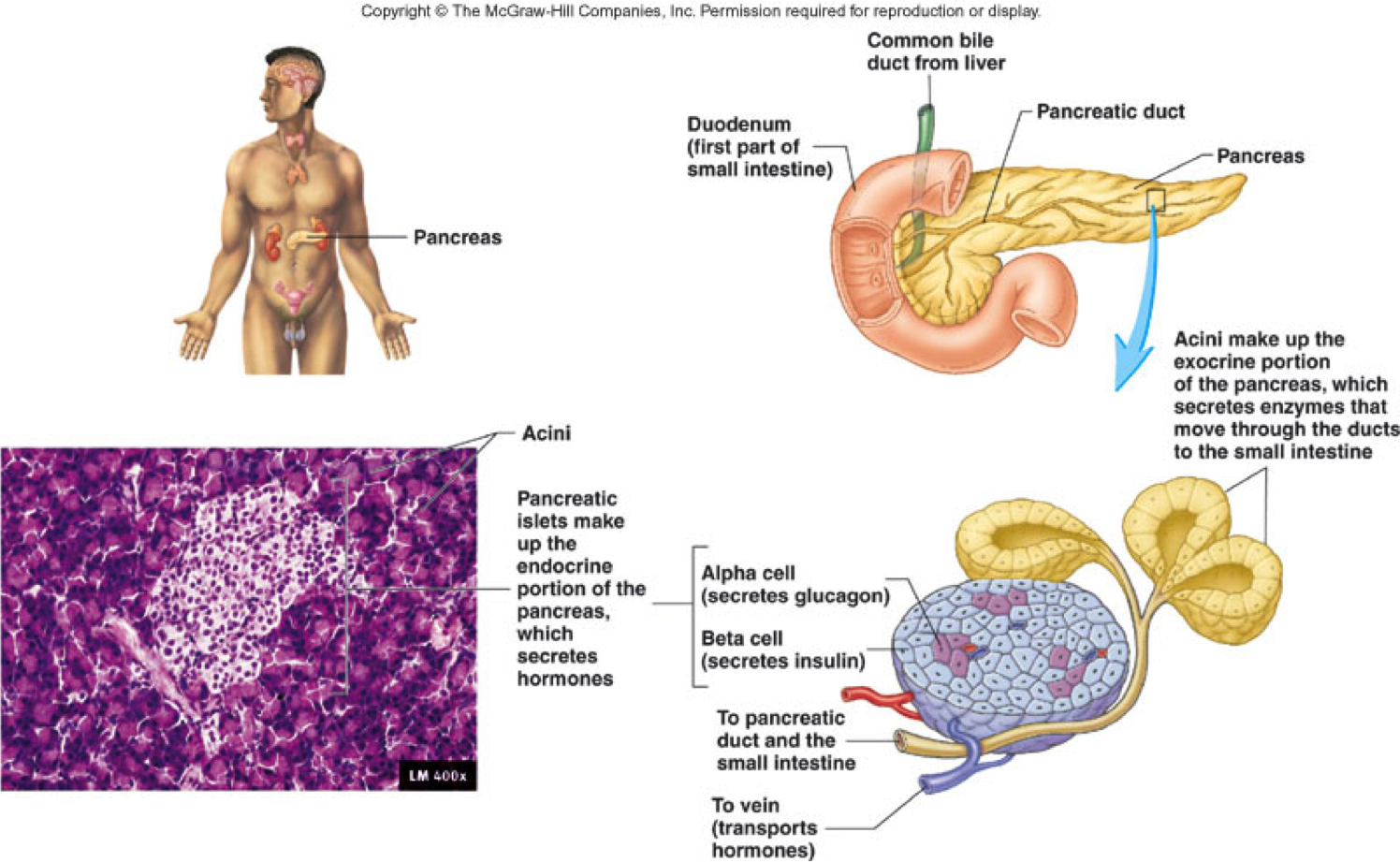



Do Any Of The Exocrine Glands Produce Hormones Socratic
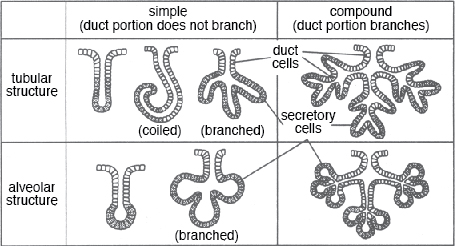



Exocrine Glands Classified As Compound Tubular Have What Kind Of Ducts Socratic
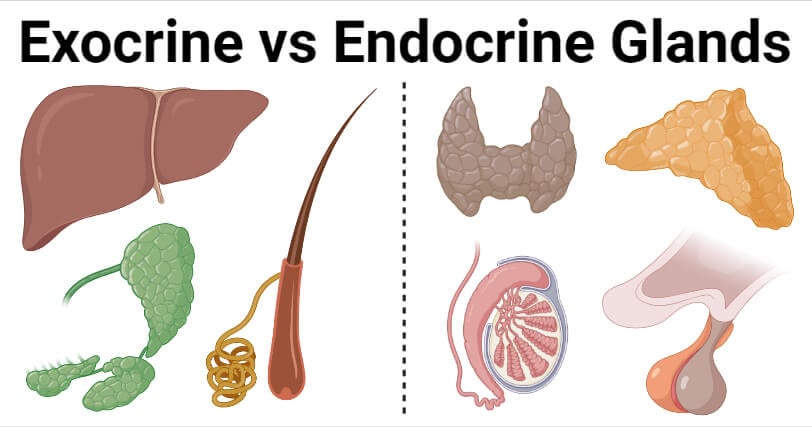



Exocrine Vs Endocrine Glands Definition 8 Differences Examples
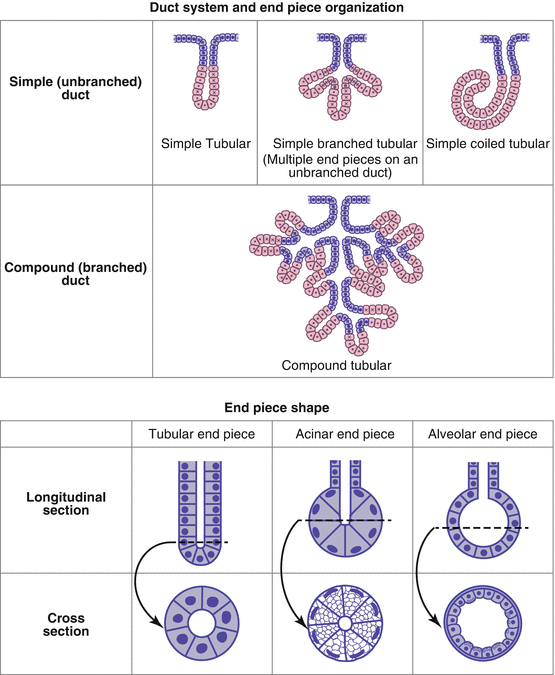



Glandular Epithelium And Glands Springerlink




Pin On School




What Is The Difference Between Endocrine Exocrine And Paracrine Glands Lorecentral




Hypothalamus Endocrine System Endocrine Pediatric Nurse Practitioner




Human Endocrine System Description Function Glands Hormones Britannica
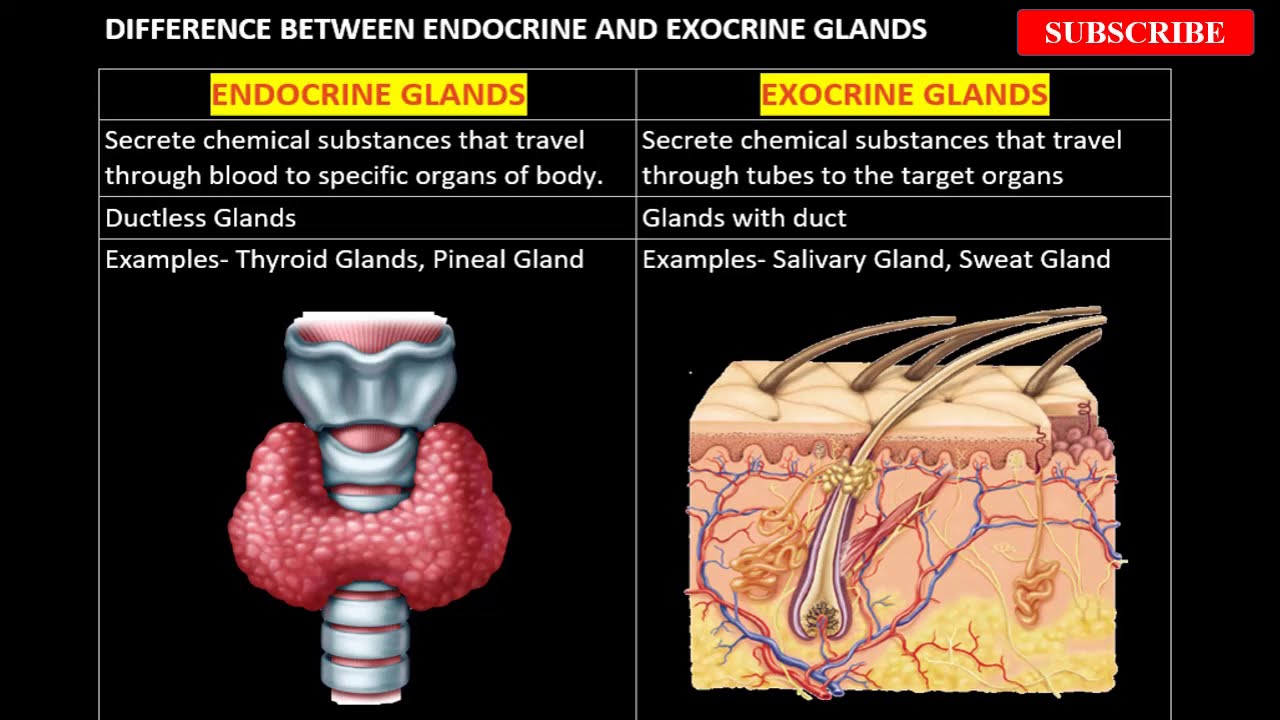



Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Biology Youtube
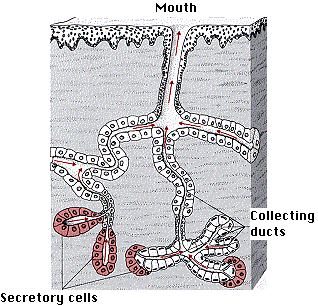



Exocrine Glands
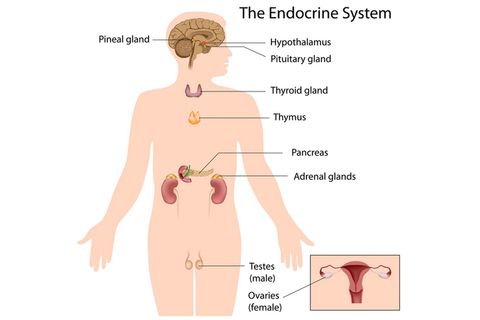



11 Surprising Facts About The Endocrine System Live Science




Prokaryotuc And Eukarytotic Cell Endocrine And Exocine Glands Essay 1
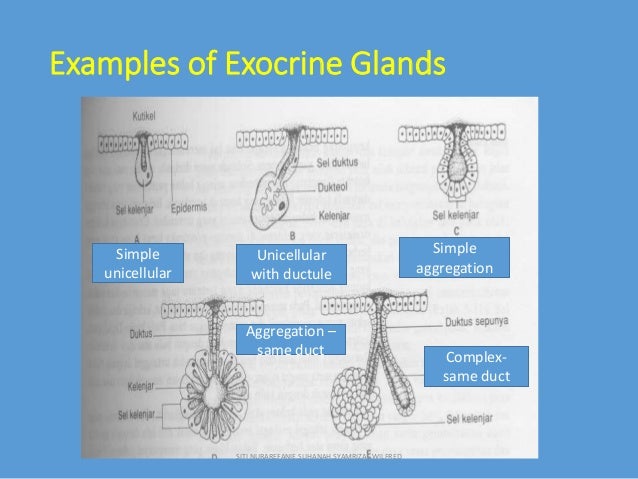



Exocrine And Endocrine Glands




Exocrine Glands Vs Endocrine Glands What Is The Difference Diffzi




Endocrine Glands Definition Examples Function Biology Dictionary




The Endocrine System 2 Contents Hormone Endocrine Exocrine Glands Types Of Hormones Functions Of Hormones The Endocrine Glands In The Human Hypothalamus Ppt Download



Significance Of Endocrine Vs Exocrine Glands Total Assignment Help




The Endocrine System Definition Ppt Video Online Download




What Is The Difference Between An Endocrine And An Exocrine Gland Brainly In
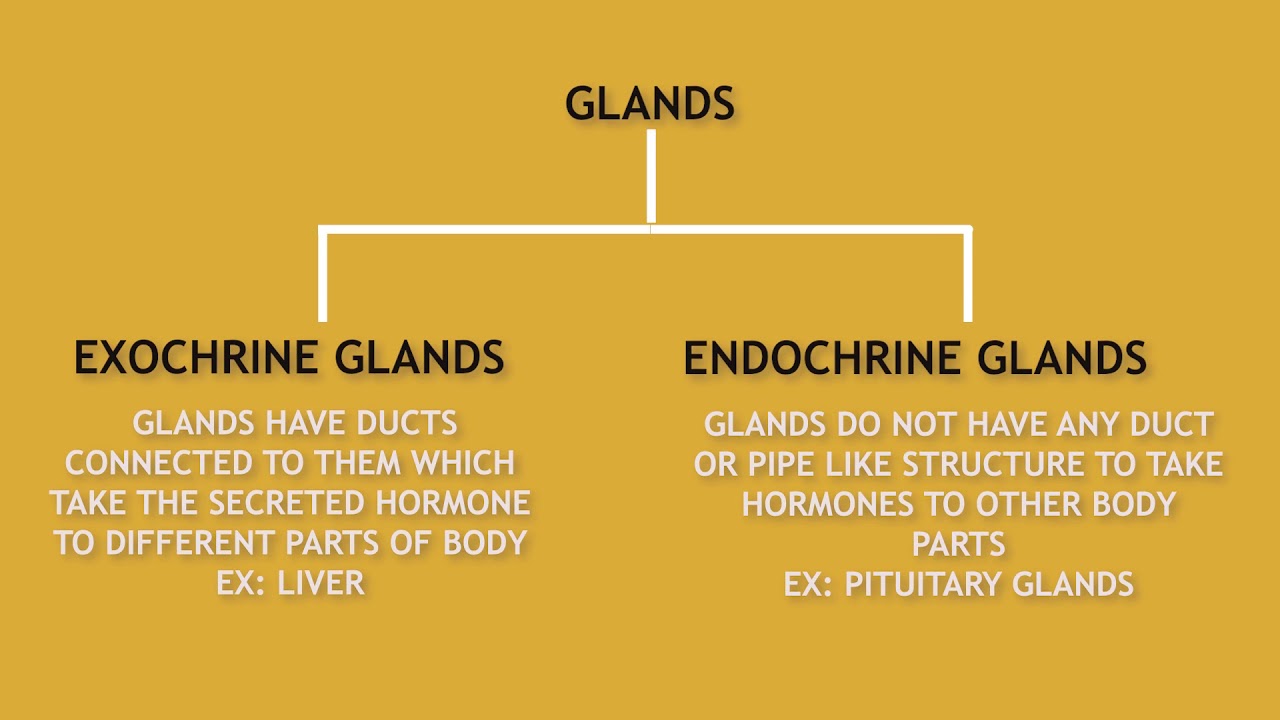



Hormones Secretion Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Youtube




Parts Of Endocrine System Different Types Of Hormones And Their Functions Biology




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll



Key Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands You Should Know New Health Advisor
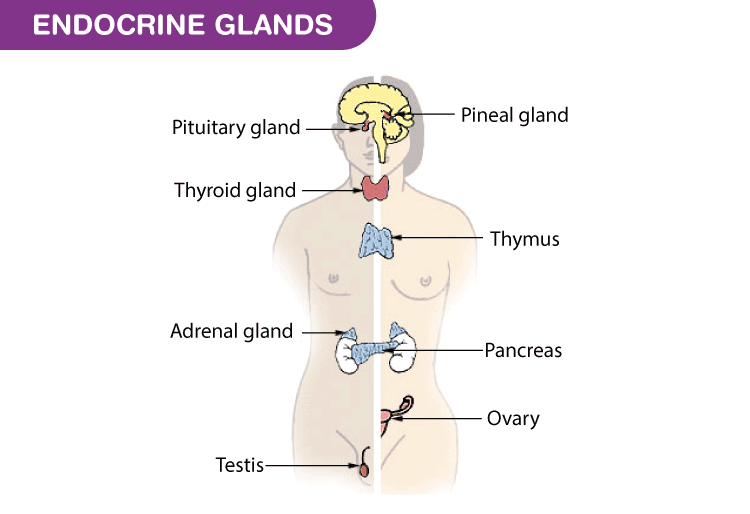



Endocrine System List Of Endocrine Glands Functions Byju S




Cc 2 Lec Compre Pdf Hormone Pancreas




Endocrine Glands And The General Principles Of Hormone Action Pdf Free Download




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll
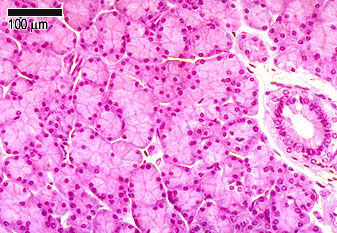



Glandular Tissue The Histology Guide
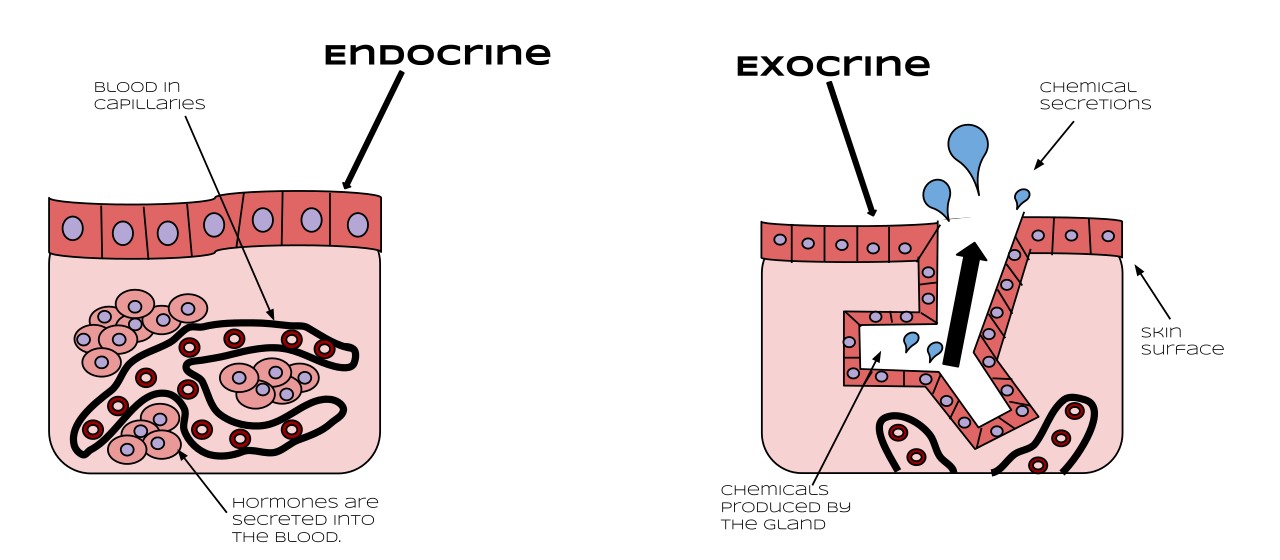



File Endocrine Vs Exocrine Svg Wikimedia Commons



2
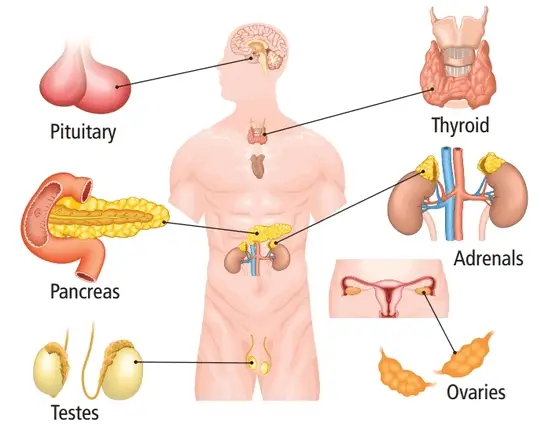



Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Difference Guru




Distribution Of Connexins In Rat Endocrine And Exocrine Glands As Download Table
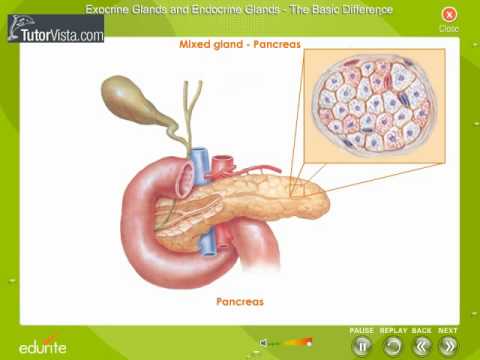



Exocrine Gland And Endocrine Glands Youtube




Exam 1 Lecture 8 Histology Epithelial Glands I Flashcards Quizlet
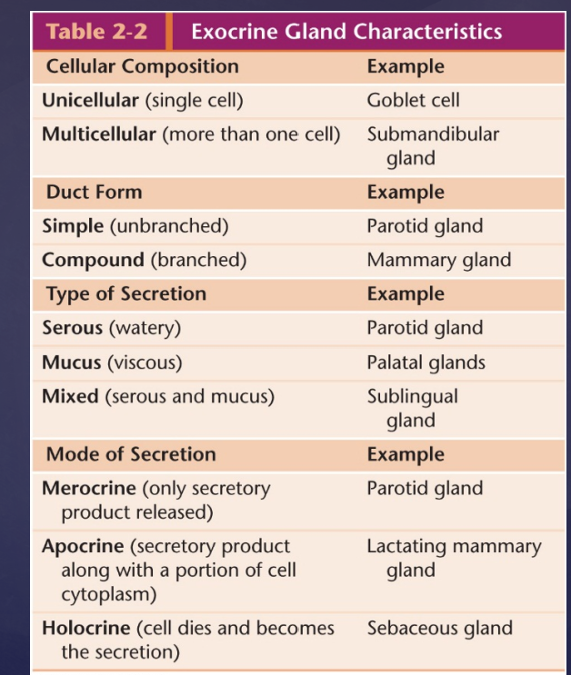



Print Vertibrate Histology Test 1 Flashcards Easy Notecards




Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Differences Function Terms Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Class 10 Control And Coordination Short Answers Freeguru Helpline




Significance Of Endocrine Vs Exocrine Glands Total Assignment Help




Lesson Explainer Hormonal Control In Humans Nagwa
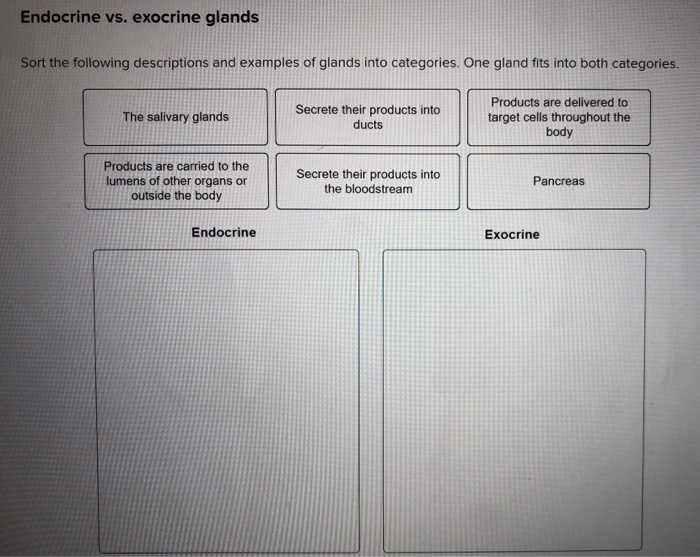



Solved Endocrine Vs Exocrine Glands Sort The Following Chegg Com




Exocrine Glands Bioninja




Glands Hormones Oestrogen Glucagon Adrenaline Insulin Testosterone Syllabus
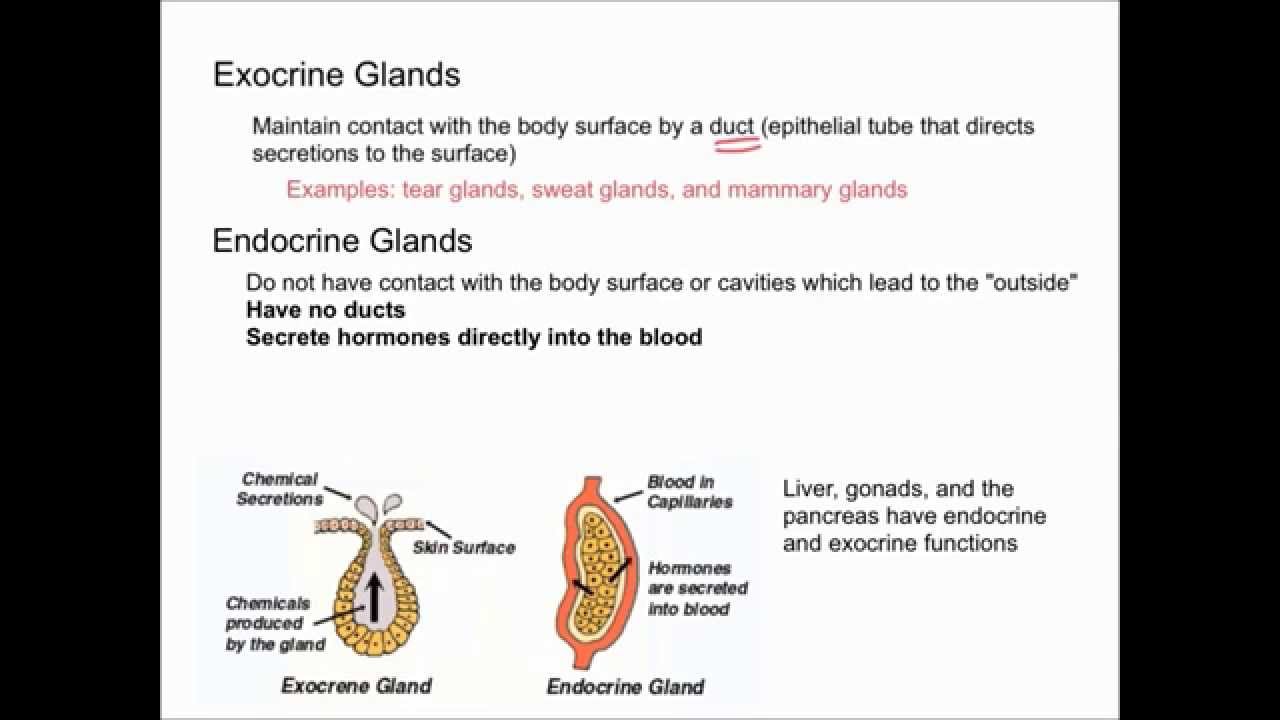



Endocrine Vs Exocrine Glands Youtube




Chapter 13 The Endocrine System Ppt Download




What Is The Endocrine System Us Epa




Endocrine System Bioninja




Chapter 13 The Endocrine System Ppt Download




Difference Between Exocrine Glands And Endocrine Glands
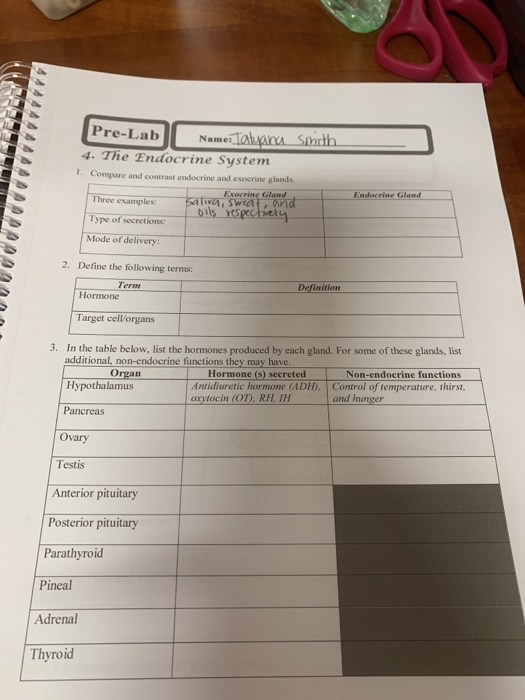



Solved Pre Lab Namei Talyana Smith 4 The Endocrine System Chegg Com



Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Definition Types Features Functions



Pancreas



Glandular Epithelia Endocrine Glands Secretes Hormones Into Directly




Endocrine System Remember Your Nervous System Senses Impulses




Endocrine System Major Hormone Secreting Structures The Endocrine




Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Differences Function Terms Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Glandular System Notes Videos Qa And Tests Grade 10 Science Human Nervous And Glandular Systems Kullabs




Types Of Glands Definition Examples Diagrams




Human Endocrine System Definition Major Endocrine Glands Their Functions




Endocrine System 1 Overview Of The Endocrine System And Hormones Nursing Times



Difference Between Exocrine And Endocrine Difference Between
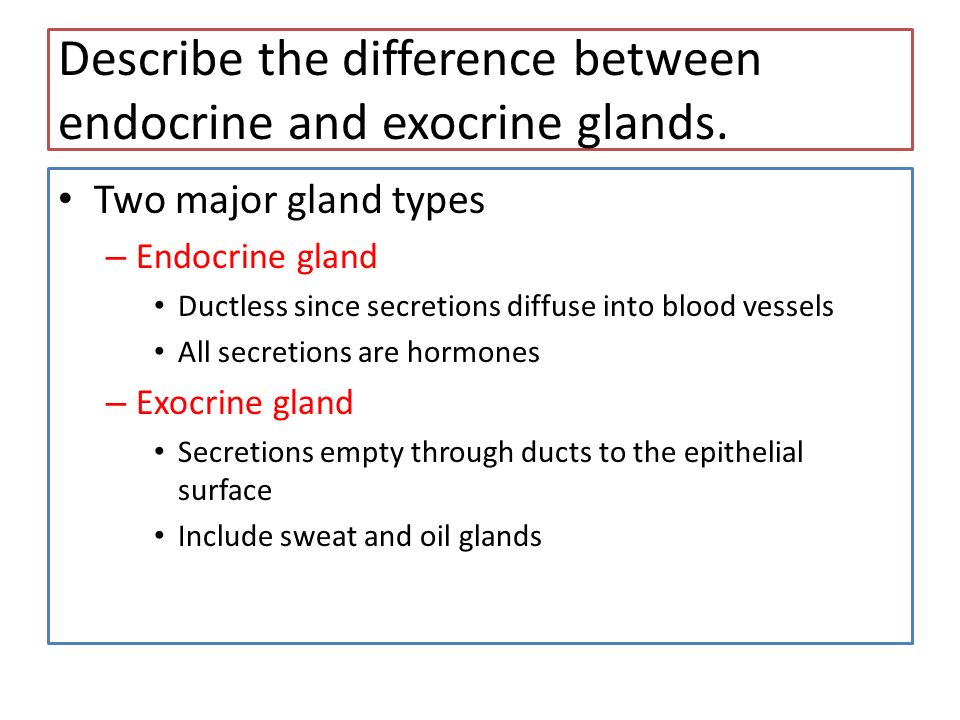



The Endocrine System And Hormone Function An Overview Define Hormone And Target Organ Describe How Hormones Bring About Their Effects In The Body Explain Ppt Video Online Download




The Importance Of Exocrine And Endocrine Glands In Human Body Ppt




Exocrine And Endocrine Glands




Adrenaline Insulin Glucagon Oestrogen Testosterone Glands Hormones Ppt Download




Pin On Chapter 5 Histology




Endocrine System 1 Overview Of The Endocrine System And Hormones Nursing Times
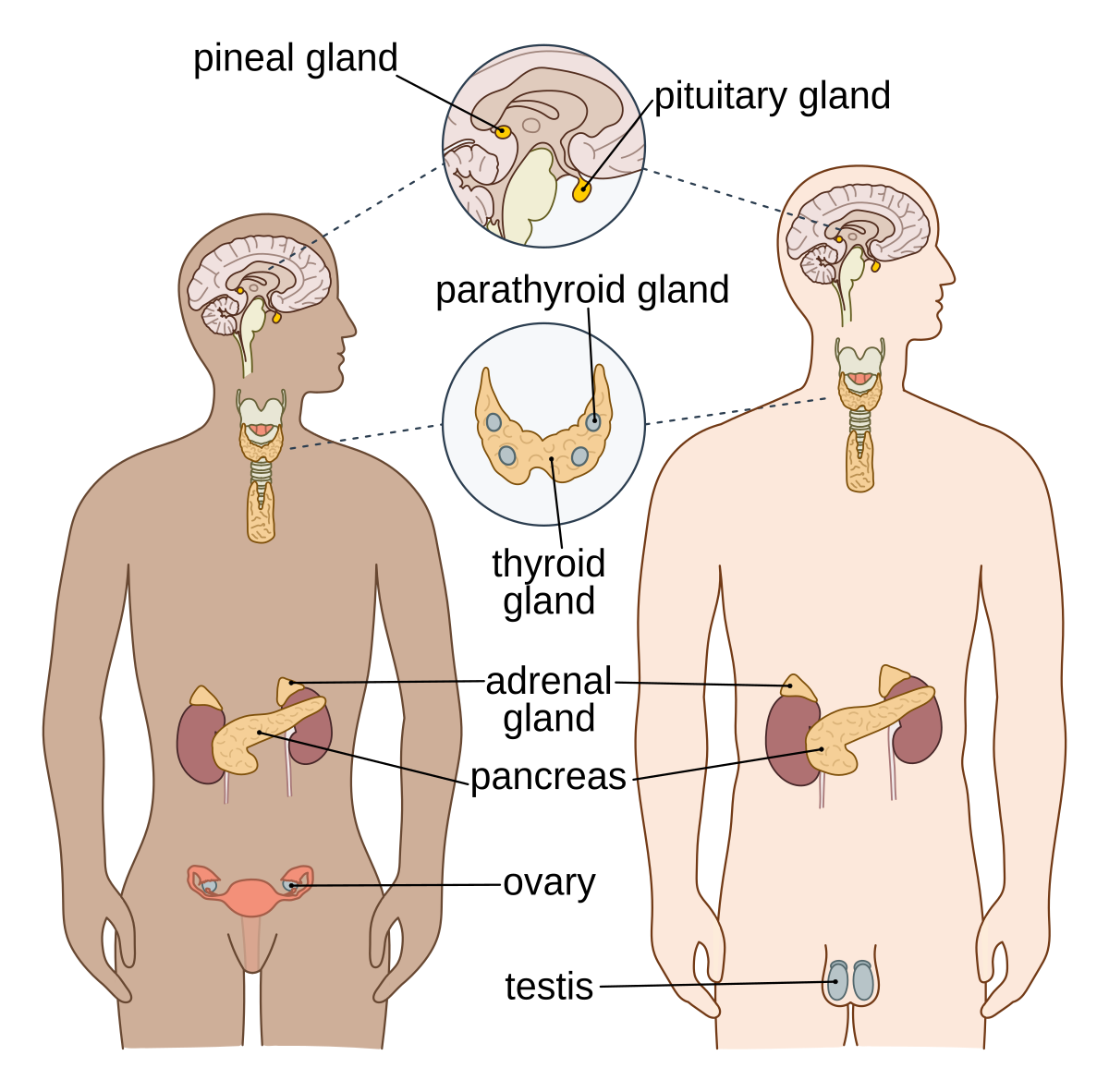



Endocrine System Wikipedia




Distribution Of Connexins In Rat Endocrine And Exocrine Glands As Download Table
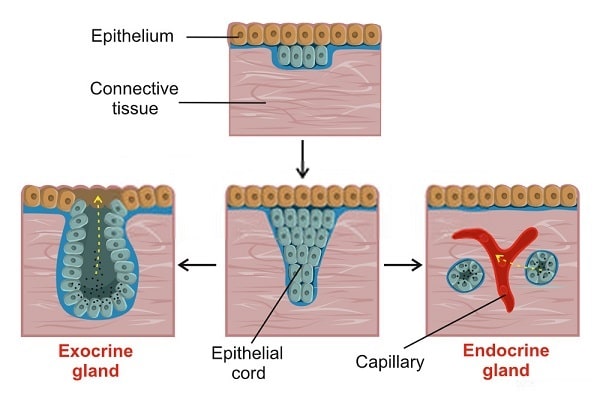



15 Types Of Glands In Human Body Their Functions
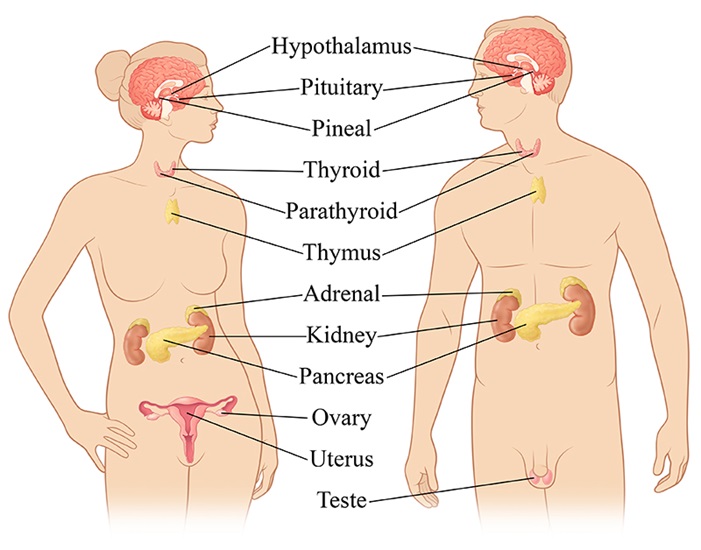



Is The Parathyroid An Endocrine Gland Are Sweat Glands Endocrine Glands Socratic



1



Study Notes




Types Of Glands Definition Examples Diagrams




Advik Science The Human Body Has Many Glands Which Facebook
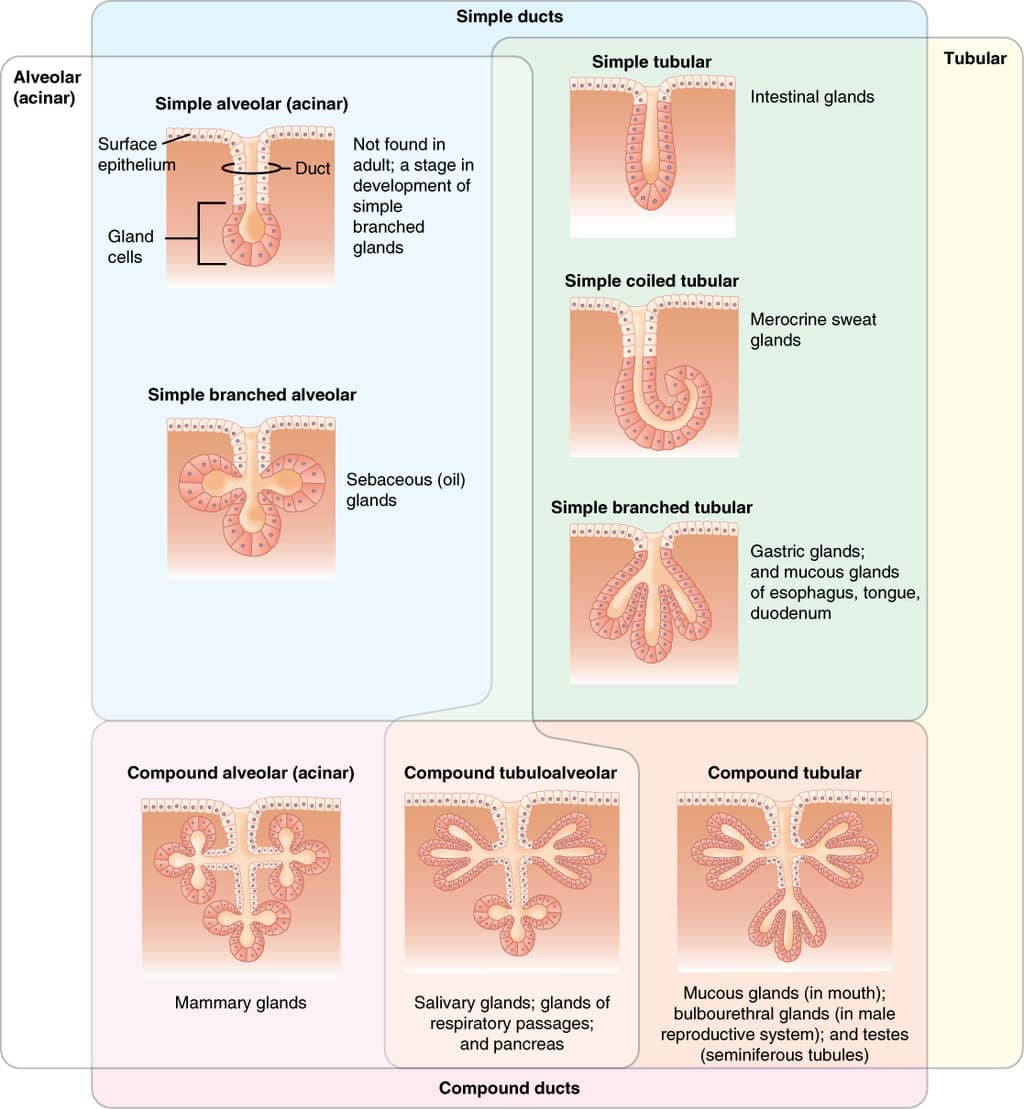



Structure Of Glands Exocrine Endocrine Histology Teachmephysiology



1
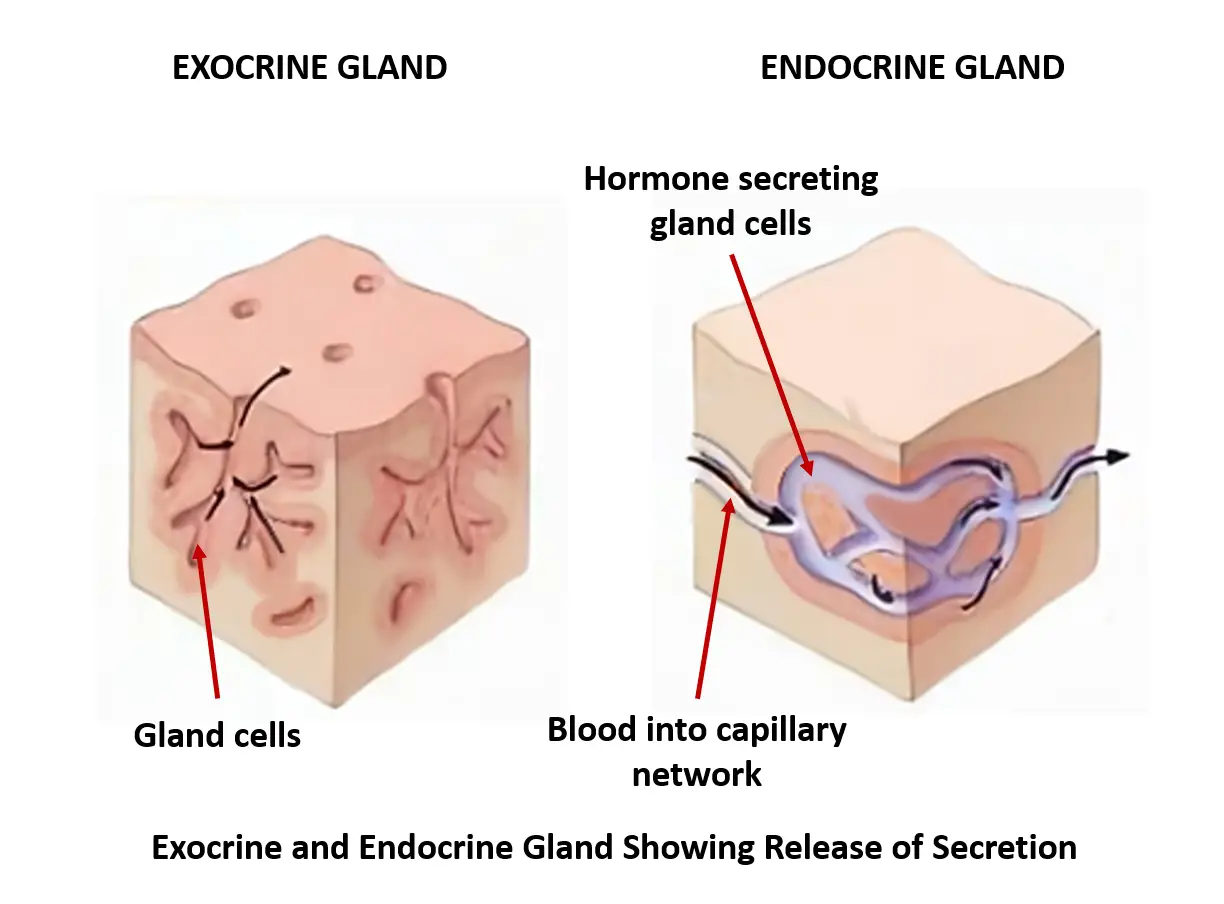



Exocrine Vs Endocrine What Is The Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine You Ask We Answer
コメント
コメントを投稿